链式队列的实现
用链表来实现的队列也称为链式队列,在链式队列中也用指针front与rear分别指示队头与队尾,在队头front处删除元素,在队尾rear处插入元素。与顺序队列不同,链式队列的rear指针指向最后一个元素,如图1所示。
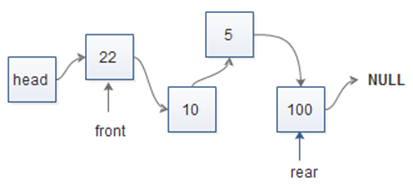
图1 链式队列
其具体实现如例1所示。
例1
LinkQueue.h //头文件
1 #ifndef _LINKQUEUE_H
2 #define _LINKQUEUE_H
3
4 typedef struct Node * pNode;
5 typedef struct Queue * LQueue; //相当于定义头结点pHead
6 struct Node
7 {
8 int data; //数据域
9 pNode next; //指针域
10 };
11
12 struct Queue //头结点
13 {
14 pNode front; //指向头结点,相当于链表中头结点里的next指针
15 pNode rear; //指向尾结点
16 int length; //队列长度
17 };
18
19 LQueue Create(); //创建队列
20 int getLength(LQueue Lq); //获取长度
21 int IsEmpty(LQueue Lq); //判断是否为空
22 void Insert(LQueue Lq, int val); // val元素入队
23 int GetHead(LQueue Lq); // 获取队头元素
24 pNode Del(LQueue Lq); // 出队
25 void Clear(LQueue Lq); // 将队列Lq清空
26 #endif //_LINKQUEUE_H
LinkQueue.c //函数实现文件
27 #include "LinkQueue.h"
28 #include <stdio.h>
29 #include <stdlib.h>
30
31 LQueue Create() //创建队列
32 {
33 LQueue Lq = (LQueue)malloc(sizeof(struct Queue)); //为头结点分配空间
34 Lq->front = NULL;
35 Lq->rear = NULL;
36 Lq->length = 0;
37 }
38
39 int getLength(LQueue Lq) //获取长度
40 {
41 return Lq->length;
42 }
43
44 int IsEmpty(LQueue Lq) //判断是否为空
45 {
46 if (Lq->length == 0)
47 return 1;
48 return 0;
49 }
50
51 void Insert(LQueue Lq, int val) //入队
52 {
53 pNode pn = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); //为val值分配结点
54 pn->data = val;
55 pn->next = NULL;
56 //如果队列为空,则将pn结点插入到头结点后
57 if (IsEmpty(Lq))
58 {
59 //Lq->next = pn;
60 Lq->front = pn; //front指向pn结点
61 Lq->rear = pn; //rear指向pn结点
62 }
63 else //如果队列不为空
64 {
65 Lq->rear->next = pn; //插入到rear指针后
66 Lq->rear = pn; //pn结点插入到rear位置处
67 }
68 Lq->length++;
69 }
70
71 int GetHead(LQueue Lq) // 获取队头元素
72 {
73 if (IsEmpty(Lq))
74 {
75 printf("队列为空,无元素可取!\n");
76 return 10000;
77 }
78 return Lq->front->data;
79 }
80
81 pNode Del(LQueue Lq) //出队
82 {
83 if (IsEmpty(Lq))
84 {
85 printf("队列为空,删除错误!\n");
86 return NULL;
87 }
88 pNode pTmp = Lq->front;
89 Lq->front = pTmp->next;
90 Lq->length--;
91 return pTmp;
92 }
93
94 void Clear(LQueue Lq) // 将队列Lq清空
95 {
96 //回到初始状态
97 Lq->front = NULL;
98 Lq->rear = NULL;
99 Lq->length = 0;
100 printf("队列已经清空!\n");
101 }main.c //测试文件
102 #include <stdio.h>
103 #include <stdlib.h>
104 #include "LinkQueue.h"
105
106 int main()
107 {
108 LQueue Lq = Create();
109 srand((unsigned)time(0));
110 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
111 Insert(Lq, rand() % 100);
112 printf("队列长度:%d\n", getLength(Lq));
113 printf("队头元素:%d\n", GetHead(Lq));
114 printf("队头元素 出队元素\n");
115 while (getLength(Lq) > 0) //出队列,循环条件是队列不为空
116 {
117 int ret = GetHead(Lq); //获取队头元素
118 printf(" %d ", ret);
119 ret = Del(Lq)->data; //出队列
120 printf("%d\n", ret);
121 }
122
123 Clear(Lq); //清空队列
124 system("pause");
125 return 0;
126 }运行结果如图2所示。
图2 例1运行结果
在例1中,我们定义了一个struct Queue,它相当于链表中的头结点;
在Queue中定义了两个pNode类型的指针:front和rear,front指向队头结点,相当于链表中头结点里的next指针;rear指向队列尾部的结点,这一点与顺序队列不同,在顺序队列中,rear指向最后一个元素后面的空位,而在本例链式队列的实现中,我们将rear指向了最后一个元素结点。
在LinkQueue.c文件中,当向队列中插入元素时,先判断队列是否为空。如果为空,则把元素结点插入到头结点后,front与rear都指向这个新结点;如果不为空,则将新元素结点插入到rear之后,然后将rear指向新结点。
当删除元素时,将front指向被删除结点后面的一个结点,因为只从头删除,所以简单两步即可。
